Content
It is not useful or necessary to record accrued interest when the amount to be accrued is immaterial to the financial statements. Recording it under these circumstances only makes the production of financial statements more complicated than should be the case, and introduces the risk of errors. Our content is not intended to provide legal, investment or financial advice or to indicate that a particular Capital One product or service is available or right for you.
Accrued interest is a part of the accrual-based accounting system. When interest becomes due, whether payable or receivable, it is recorded in the books of accounts, not on the date it is paid or received. This is to satisfy the matching concept and the revenue recognition principle of accounting.
Please Sign in to set this content as a favorite.
The main variables that affect the calculation are the period between interest payments and the day count convention used to determine the fraction of year, and the date rolling convention in use. Accrued interest is an important consideration when purchasing or selling a bond. Bonds offer the owner compensation for the money they have lent, in the form of regular interest payments. These interest payments, also referred to as coupons, are generally paid semiannually.
The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. If you want to find your annual interest, you need to divide your interest rate compounded over 12 months. The flat price can be calculated by subtracting the accrued interest part from the full price, which gives a result of $1,028.08.
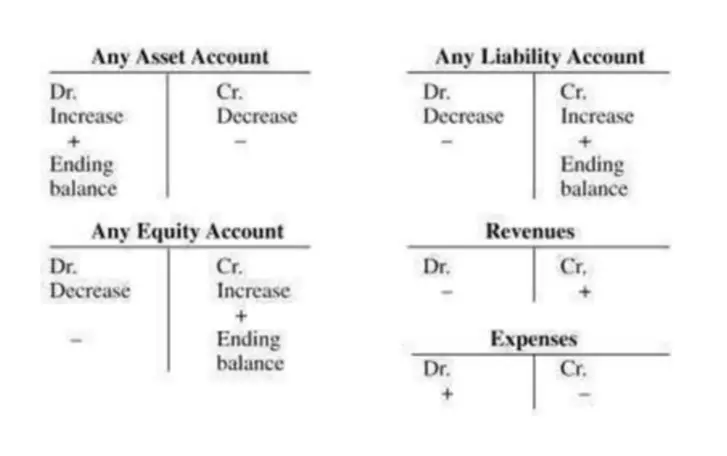
How to Account for Accrued Interest
Daily interest is generally rare in the case of mortgages, though. You’re much more likely to see daily interest accrual with credit cards. It repeats the accrual process each monthly period based on the new loan principal balance.
This is because the company has earned the interest, but has not yet received the payment. Accrued interest is the amount of interest that has accumulated on a loan or investment but has not yet been paid or received. In simpler words, accrued interest means the interest that is earned but not yet received or paid out. It’s important to keep track of accrued interest because it will eventually need to be paid or received.
Daily Accrual
This type of interest involves calculating interest not only on the original principal balance but also on any interest that has accrued since the last payment was made. This means that interest can grow more quickly over time, as the interest itself also earns interest. Overall, accrued interest is a way to keep track of how much interest has been earned or owed over a certain period of time, even if it hasn’t been paid out or received yet. In all investing, it is important to have a firm grasp on the basics. You probably won’t have to do the calculations manually, but just knowing how much interest accrues on an account is important for borrowers and lenders. On the other hand, if you’re thinking about buying or selling an investment, you may need to calculate the amount of accrued interest to make sure the transaction is fair.
Power its potential with one of our business credit cards, like Ink Business Preferred℠, Ink Business Unlimited℠ or Ink Business Cash℠. Enjoy the convenience of earning cash back with Chase Freedom® or Chase Freedom Unlimited®. A higher purchase APR (annual percentage rate) means you will owe more in interest if you carry a balance, while a lower purchase APR means you will owe less. The reason why credit card balances can quickly build up on cards with high APRs is because of compounding interest charges that occur on a daily basis. Accrued interest is generally only recorded once at the end of the accounting period.
Our Services
By paying the minimum you keep your account in good standing but you do not avoid accruing interest. The exception to this is if you have a card with a 0% introductory APR, which usually is for a set period of time. Once that introductory period https://www.bookstime.com/articles/accrued-interest is done, your APR resets and you begin accruing interest on the balance. For example, a Treasury bond with a $1,000 par value has a coupon rate of 6% paid semi-annually. The bond matures in two years, and the market interest rate is 4%.
How do you accrue interest?
- Divide the number of days you're examining from the maximum number of days in a year, which is 365.
- Multiply the interest rate by the divided result.
- Multiply the number you attained in step two by the loan amount.
- Examine your final result.
Once the next accounting period rolls around, these adjusting entries would be reversed. As the end of the accounting period comes near, the borrower and lender must adjust their ledger to account for the interest that accrued. Once the interest amount is paid in cash, the journal entries will be adjusted to reflect that the borrower has paid the owed interest to the lender. Understanding how the interest rate and APR work can make all the difference in controlling your debt.
Travel cards
Finally, multiply the monthly interest rate by the average daily balance in order to calculate the interest that accrued during the month. If the account’s principal balance did not fluctuate during the month, such as with a typical mortgage, the average daily balance is simply equal to the starting balance. Another key thing to know is that, with student loans, you may not always have to pay that accrued interest. There are a few ways this can work for people with federal student loans. When it comes to loans, accrued interest is the amount of unpaid interest that has built up since you last made a payment. In the context of student loans, for example, interest may begin accruing at the moment your loan is disbursed and continue to accrue until you pay it off.
This enables the accrued interest to be included in the lender’s balance sheet as an asset (and in the borrower’s balance sheet as a provision or liability). However if the accounts use the market price as derived by method 2 above, then such an adjustment for accrued interest is not necessary, as it has already been included in the market price. Suppose that interest for a business loan is payable on the 15th of each month, but your accounting period ends on the 30th of this calendar month. In this case, you will accrue 15 days of interest, from the 16th to the 30th. This figure would be added up and posted as part of your adjusting journal entries, and then reversed on the first day of the next month when the cash transaction is received. Imagine that a business takes out a loan to purchase company equipment.
money management tips to improve your finances
He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com. Once you have viewed this piece of content, to ensure you can access the content most relevant to you, please confirm your territory. Get up and running with free payroll setup, and enjoy free expert support. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Finance Strategists is a leading financial literacy non-profit organization priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. It would not be correct to wait until the due date of 28 February to recognize the interest revenue earned through 31 December 2019.
- The bond issuer is responsible for paying the accrued interest at a later date.
- Then, find out how to set up the journal entry for borrowers and lenders and see examples for both.
- Accrued interest works by accumulating overtime on a loan or investment that has an interest rate attached to it.
- This figure should also be reported on the balance sheet as either an asset or liability.
- If you entered «Never» on the left, try selecting a different frequency and enter a manageable payment amount.
- Some lenders capitalize unpaid interest – add it to the principal amount of your loan.